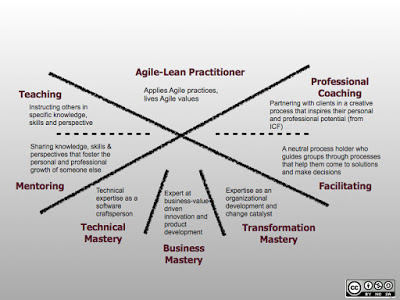
What does an Agile Coach?

An agile coach has three main areas of activity:
- Foster Autonomy
-
Teach and support the team and individuals to be autonomous within the given boundaries of the organization and its processes.
- Create Ground for Motivation
-
Help teams to maximize their autonomy, individual mastery and make sure the team has a purpose.
- Provide Coaching
-
Support teams and individuals to identify potential with their roles and within the agile organization and improve.
How Can You Do It?
- Lateral Leadership
-
Mediating the team through conflicts and helps them with making decisions and foster the team’s self-organization. After a few months, a team shall have jelled.
- Facilitation
-
Facilitate meetings for the team, including preparing, moderation and post-processing for the agile process as well as the supporting agile organization. After a year of working with a team, the team members shall be empowered to run regularly all events without you attending.
- Teaching
-
Teach teams agile practices and lateral leadership. A central area is technical excellence and software craftsmanship. Long-lasting teaching shall concentrate on values: Scrum values and principles, LeSS principles, Agile manifesto and the associated 12 principles.
- Impediments
-
Actively identify impediments and foster their removal. Consult the Scrum guide: You must select one impediment after each retrospective and add it as a high-priority item in the next Sprint backlog. This mechanism insures continuous improvement.
To ensure continuous improvement, it includes at least one high-priority way in which the team works, identified in the previous Retrospective meeting.
- Culture
-
Establish a culture of inspecting and adapting for teams. Create a structure to establish a continuous improvement process - also meaning establish a tolerance to failure -, advocate transparency, enlighten the organization of the relation between autonomy and accountability.
Ask yourself how your organization handles meritocracy.
One Approach to Coaching
Agile teams thrive with purpose, autonomy and mastery. One approach to coaching is to set your focus on
-
Understand the domain: Talk with customers and users and understand their needs. Your teams should have business expertise.
-
Master Technical Excellence: CI, CD, TDD, ATDD, pair programming, refactoring, lean UX, usability.
-
Use Process Excellence and apply Scrum, XP, LeSS by the book:
-
Discuss the core values of commitment, focus, openness, respect, and courage.
-
Present again the agile manifesto and the twelve principles.
-
Show the organization why forecast replaced commitment in the planning in the official Scrum guide [1].
-
Require a vision, a roadmap, a release plan with a story map and a refined backlog for each product and team.
-
Tell why an impediment resolution backlog item shall be part of each iteration.
-
Teach the importance of the definition of done DoD for the internal quality of the product. And explain why the definition of ready is often an anti-pattern.
-
Show why velocity is not a productivity metric.
-
Show the difference between product and output.
-
Extend the agile toolbox with Design Thinking, Lean Factory, Lean UX, DevOps.
-
Pair Scrum master and technical master to implement a craftsmanship path and achieve product quality.
-
Explore Center of Competencies to nurture your product development group.
-
Once you are a master fell free to break the rules, experiment with new rules, approaches [2, 3]. Define hypotheses and verify them empirically.
If you are coaching software development groups, acknowledge you shall possess a profound understanding of technical excellence and software development practices. I have never heard of a soccer coach not intimately knowing how the game is played.
How to Evaluate Yourself?
Skill in a competency area is not a simple binary. Skill mastery is a progression from no knowledge to unconscious mastery. Try to define if you are a beginner, practitioner, guide, or catalyst for each relevant dimension.
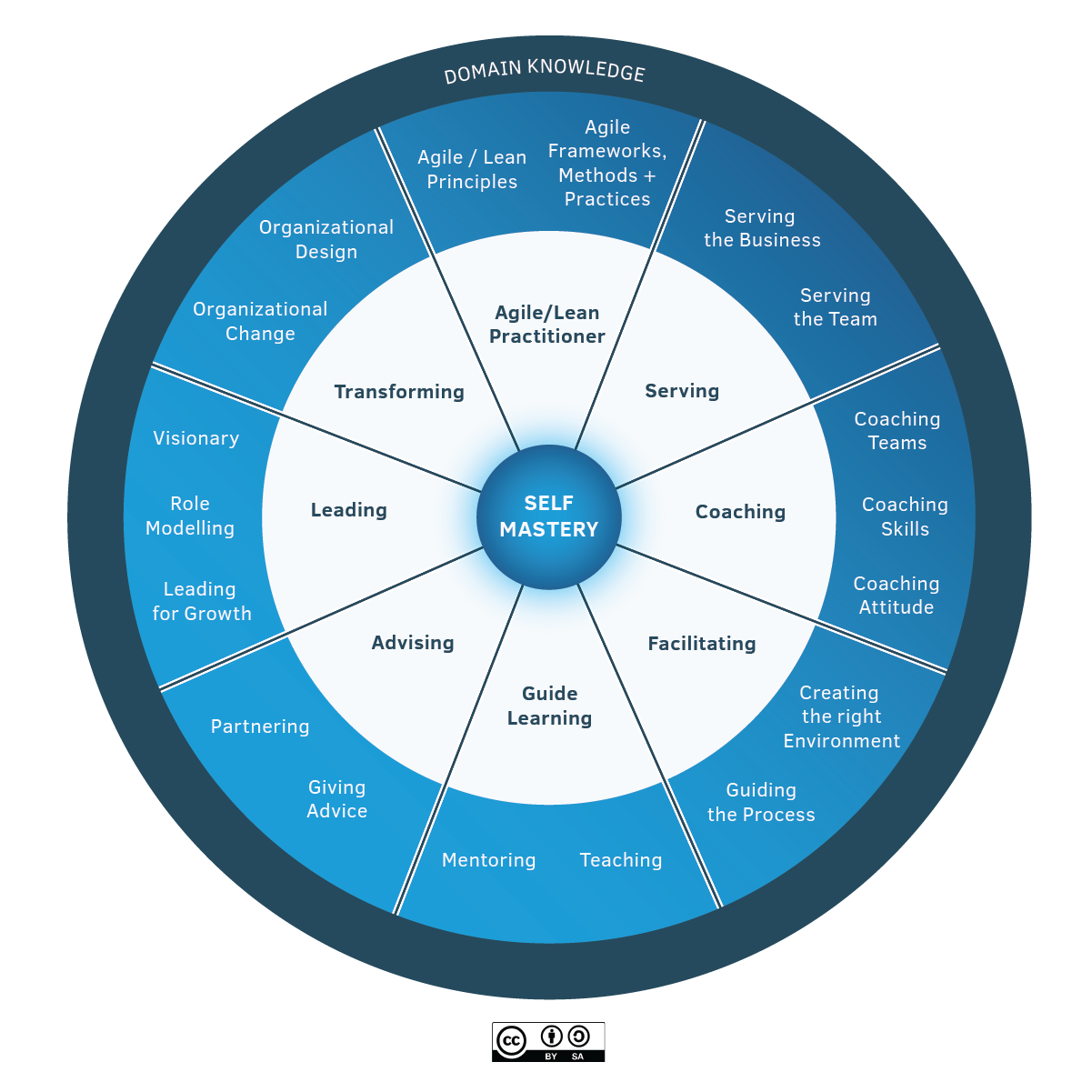
| Self-Mastery |
At the heart of great agile coaching is the need to invest in yourself through learning and reflection and take care of your well-being. Self-mastery starts with a focus on yourself, having the emotional, social, and relationship intelligence to choose how you show up in any given context. |
| Agile/Lean Practitioner |
an agile/lean practitioner has a deep and tacit understanding of the principles behind agile and lean and has experience in working with frameworks and practices of agile and lean. |
| Serving |
serving is about being concerned with the needs of the team or business over your own agenda. They do this from the stance of servant leadership, which focuses primarily on the growth and well-being of the team or business and the communities to which they belong. |
| Coaching |
coaching is partnering with a person, team, or organization (client) in a creative process to help the client to reach their goals by unlocking their own potential and understanding. A coach is able to accept the client as a whole and capable and serve their agenda ethically. |
| Facilitating |
facilitating increases the effectiveness of groups to align in a collaborative way, to interpret their context, and mutually identify the most valuable outcomes desired. A facilitator has the skills to create a neutral environment of openness, safety, and innovation in a group setting. |
| Guide to Learning |
guide to learning is about effectively growing an individual, a group, or a team skills and enabling them to be competent and resourceful. With this competency, you choose the most effective learning method to help the learners achieve their learning objectives and inspire future learning. |
| Advising |
advising is the ability to bring your experience, insights, and observations to guide the client towards a shared understanding of the value that can help them to achieve sustainable success, even after you have moved on. As a trusted adviser, you are invested in the success of the client, creating a long-term and sustaining relationship with the client. |
| Leading |
leading is about being the change you want to see to make the world a better place. As a leader, you are capable of catalyzing growth and inspiring others to realize the shared vision. |
| Transforming |
transforming is guiding sustainable change that will allow the individual teams and the organization to be more effective and learn how to change for themselves through leading, facilitation, coaching, facilitating learning, and advising. |
Links
-
[1] Why Professional Coaching Matters to an Agile Coach. Mikael Brodd. Crisp. 2021
References
[1] G. Verheyen, Scrum - A Pocket Guide, Third. Van Haren Publishing, 2021 [Online]. Available: https://www.amazon.com//dp/B0DFHNW45Q
[2] Z. Sochova, The Great Scrum Master. Addison Wesley, 2016 [Online]. Available: https://www.amazon.com/dp/013465711X
[3] M. Cohn, Succeeding with agile. Addison-Wesley, 2010 [Online]. Available: https://www.amazon.com/dp/0321579364