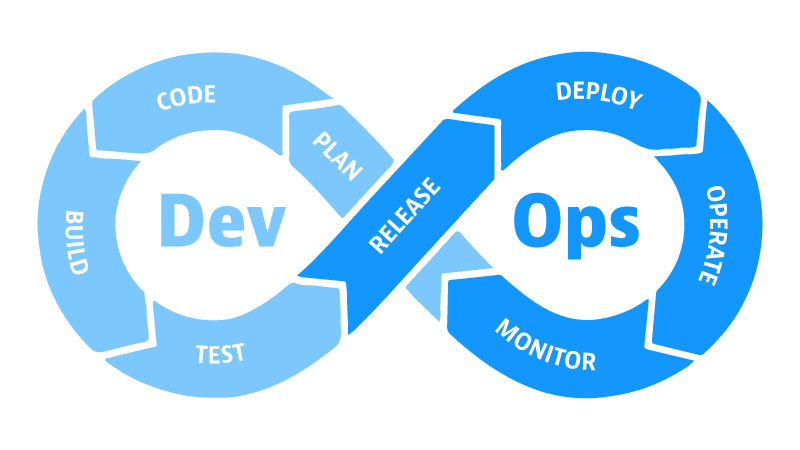
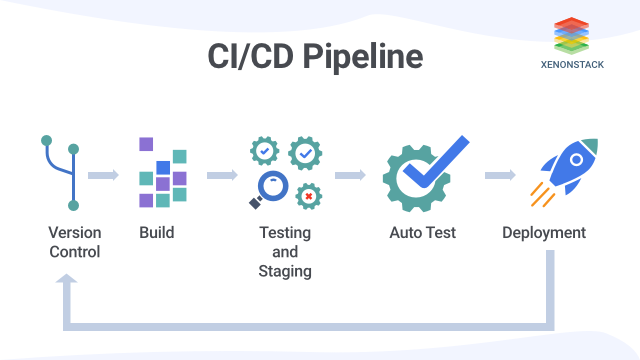
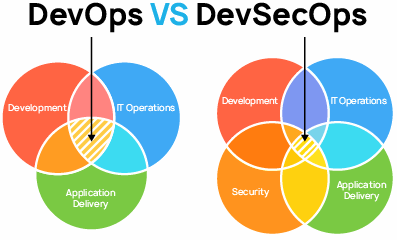
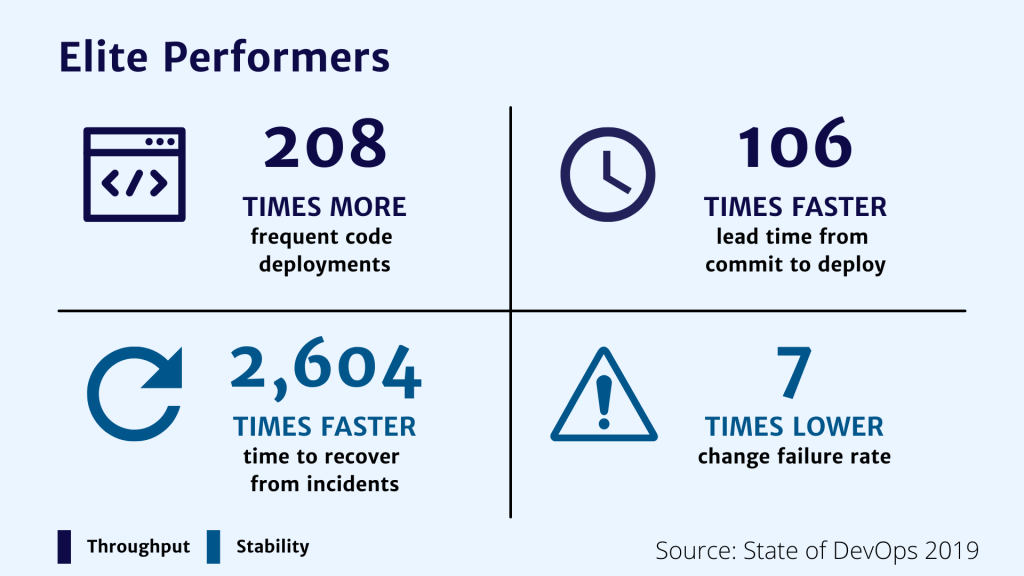
DevOps initiatives create cultural changes in companies by transforming the way operations, developers, and testers collaborate during the development and delivery processes.
Getting these groups to work cohesively is a critical challenge in enterprise adoption.
DevOps is as much about culture, the toolchains are only instruments to implement the approach.
Organizational culture is a strong predictor of IT and organizational performance.
Cultural practices such as information flow, collaboration, shared responsibilities, learning from failures, and encouraging new ideas are central to DevOps.
Team-building and other employee engagement activities are often used to create an environment that fosters this communication and cultural change within an organization.
DevOps as a service approach allows developers and operations teams to take greater control of their applications and infrastructure without hindering speed.
It also transfers the onus of owning a problem on to the development team, making them much more careful in their stride.
The 2015 State of DevOps Report discovered that the top seven measures with the strongest correlation to organizational culture and successful DevOps are:
-
Organizational investment,
-
Team leaders' experience and effectiveness,
-
Continuous delivery,
-
The ability of different disciplines development, operations, and security to achieve win-win outcomes,
-
Organizational performance,
-
Deployment pain,
-
Lean management practices.